Topics to be covered in Consumer Behavior article:
- Understand the buying habits of consumers
- Models of consumer behavior
- Recognize types of buying behavior
- Understand the buyer-decision process
- Buyer decision for new products
- Factors affecting consumer behavior
Consumer behavior
Consumer behavior refers to the actions and the decision process of the people who purchase goods and services for personal consumption
The consumer market is made up of all the final consumers who buy products or services for personal consumption.
Types of Consumers
- Consumer – is a purchaser of goods and services for immediate use or consumption.
- Customer –who purchases goods for his own use or for the use of others.
- Buyer – who purchase goods either for resale or for use in production.
- Institutional buyer – are either govt. institutions or private organizations purchase goods or service for institutional use.
Five Premises of Consumer Behavior
- Consumer behavior is purposeful and goal oriented
- The consumer has free choice
- Consumer behavior is a process
- Consumer behavior can be influenced
- There is a need for consumer education
A Model of Consumer Behavior
Marketing and stimuli
Marketing:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
Others
- Economic
- Technological
- Political
- Cultural
Buyer’s bkack box
Buyer characteristics
Buyer decision process
Buyer responses
- Product choice
- Brand choice
- Dealer choice
- Purchase timing
- Purchase amount
Quesions:
- Why companies are so interested to study consumer behavior?
- Write any three reasons?
Importance of study consumer behavior
- To make better strategies for increasing profits.
- To know the buying decisions and how consumer make consumption.
- Consistent change in consumer`s tastes or preferences
- Consumer behavior study is necessary to make pricing policies
- To avoid future market failures
Types of Buying Decision Behavior
| High involvement | Low involvement | |
| Significant differences between brands | Complex buying behavior | Variety seeking buying behavior |
| Few differences between brands | Dissonance reducing buying behavior | Habitual buying behavior |
The Buyer Decision Process

Need recognition
Occurs when the buyer recognizes a problem or need triggered by:
- Internal stimuli
- External stimuli
Information search – Sources of Information (Which source of information is more reliable to customers?)
- Personal sources—family and friends
- Commercial sources—advertising, Internet
- Public sources—mass media, consumer organizations
- Experiential sources—handling, examining, using the product
Evaluation of alternatives
How the consumer processes information to arrive at brand choices
Purchase Decision
- The act by the consumer to buy the most preferred brand
- The purchase decision can be affected by:
- Attitudes of others
- Unexpected situational factors
Post-Purchase Decision
The satisfaction or dissatisfaction that the consumer feels about the purchase Relationship between:
- Consumer’s expectations
- Product’s perceived performance
The larger the gap between expectation and performance, the greater the consumer’s dissatisfaction
Cognitive dissonance is the discomfort caused by a post-purchase conflict
The Buyer Decision Process for New Products
Adoption process is the mental process an individual goes through from first learning about an innovation to final regular use
- Awareness: The consumer becomes aware of the new product but lacks information about it.
- Interest: The consumer seeks information about the new product.
- Evaluation: The consumer considers whether trying the new product makes sense.
- Trial: The consumer tries the new product on a small scale to improve his or her estimate of its value.
- Adoption: The consumer decides to make full and regular use of the new product.
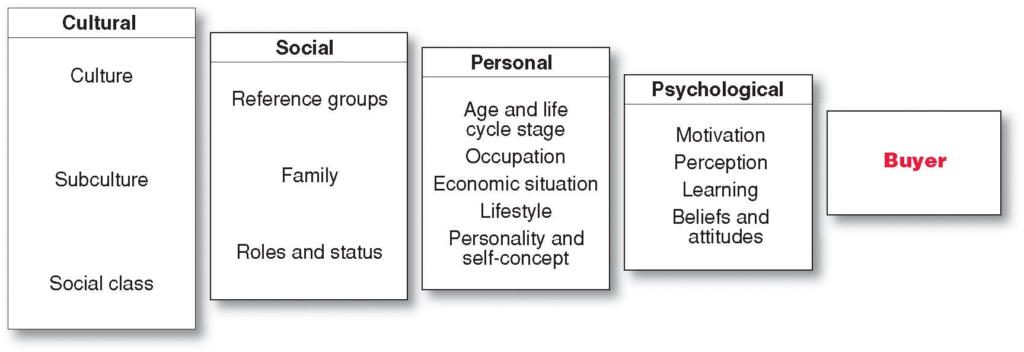
Characteristics Affecting Consumer Behavior
Culture and Sub-Culture
- Culture is the learned values, perceptions, wants, and behavior from family and other important institutions
- Subculture are groups of people within a culture with shared value systems based on common life experiences and situations
Cultural Factors
Social Class
Social classes are society’s relatively permanent and ordered divisions whose members share similar values, interests, and behaviors
Measured by a combination of occupation, income, education, wealth, and other variables
Group and Social Networks
Membership Groups
Group with direct influence and to which a person belongs
Aspirational Group
Group and individual wishes to belong to
Reference Groups
Groups that form a comparison or reference in forming attitudes or behavior
-
- Family is the most important consumer-buying organization in society
- Social roles and status are the groups, family, clubs, and organizations that a person belongs to that can define role and social status
- Online Social Networks are online
communities where people socialize or exchange information and opinions - Include blogs, social networking sites (Facebook), virtual worlds (second life)
Personal Factors
Age and life-cycle stage RBC Royal Band stages
- Youth: younger than 18
- Getting started: 18–35
- Builders: 35–50
- Accumulators: 50–60
- Preservers: over 60
Questions?
- How one child policy in China affect demand of certain product?
- If there is more old-aged people in a country, what type of product or service will be more profitable for companies?
- Occupation affects the goods and services bought by consumers.
- Economic situation includes trends in:
- Lifestyle is a person’s pattern of living as expressed in his or her psychographics
Personality and Self-Concept. Personality refers to the unique psychological characteristics that lead to consistent and lasting responses to the consumer’s environment

Psychological Factors

Psychological Factors Motivation:
- A motive is a need that is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seek satisfaction
- Motivation research refers to qualitative research designed to probe consumers’ hidden, subconscious motivations

Psychological Factors:
- Perception is the process by which people select, organize, and interpret information to form a meaningful picture of the world from three perceptual processes
- Selective attention
- Selective distortion
- Selective retention
- Selective attention is the tendency for people to screen out most of the information to which they are exposed
- Selective distortion is the tendency for people to interpret information in a way that will support what they already believe
- Selective retention is the tendency to remember good points made about a brand they favor and forget good points about competing brands

Beliefs and Attitudes
- Belief is a descriptive thought that a person has about something based on:
- Knowledge
- Opinion
- Faith
- Attitudes describe a person’s relatively consistent evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea
Referrences:
https://clootrack.com/knowledge_base/what-is-consumer-behavior/