Products, Services, and Brands Topic Outline:
- Define product and describe the major classifications of products and services.
- Describe the decisions companies make regarding their individual products and services, product lines, and product mixes.
- Identify the four characteristics that affect the marketing of services and the additional marketing considerations that services need.
- Discuss branding strategy—the decisions companies make in building and managing their brands.
- How to build a brand? And what makes a good brand?
What Is A Product?
Product is anything that can be offered in a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a need or want.
What Is A Service?
Service is a product that consists of activities, benefits, or satisfactions and that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.
Products, Services, And Experiences
Products and services are becoming more competitive in modern business.
Businesses are now creating and managing customer experiences with their brands or company.
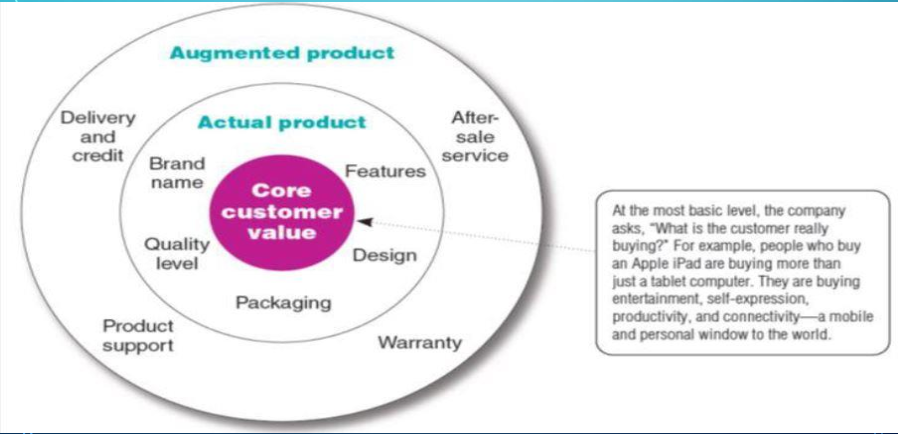
Product And Service Classifications
1 – Consumer products
Consumer products are products and services bought by final consumers for personal consumption.
- Convenience products
- Shopping products
- Specialty products
- Unsought products
Convenience products
Convenience products are consumer products and services that the customer usually buys frequently, immediately, and with a minimum comparison and buying effort.
- Newspapers
- Candy
- Fast food
Shopping products
Shopping products are less frequently bought consumer products and services that the customer compares carefully on suitability, quality, price, and style.
- Furniture
- Cars
- Appliances
Specialty products
Specialty products are consumer products and services with unique characteristics or brand identification for which a significant group of buyers is willing to make a special purchase effort.
- Medical services
- Designer clothes
- High-end electronics
Unsought products
Unsought products are consumer products that the consumer does not know about or knows about but does not normally think of buying.
- Life insurance
- Funeral services
- Blood donations
2 – Industrial products
Industrial products are those products purchased for further processing or for use in conducting a business.
- Materials and parts: include raw materials and manufactured materials and parts.
- Capital items: are industrial products that aid in the buyer’s production or operations.
- Supplies and services: include operating supplies, repair and maintenance items, and business services. Hardware, software and services. office furniture and equipment, commodities, vehicle parts, specialist requirements.
FOUR characteristics that affect the marketing
- Organization marketing
- Person marketing
- Place marketing
- Social marketing
Organization marketing
- Organization marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change the attitudes and behavior of target consumers toward an organization.
Example: Samsung’s marketing strategy related to their overall organizational strategy. Slogan of Samsung Company says that “Everyone’s invited”. As per the market researches, the main strengths of Samsung are identified as:
- Strong global business network
- Huge trustworthiness of Brand Name
- Innovative changes and inspiring new styles
- The awards it is continuously receiving
- Samsung has strong global competitiveness with its service and sales. Samsung can utilize its strengths available as major threats to other organizations. Samsung can effortlessly improve its image by the promotional Adds and quality products.
- Samsung Electronics vision for the new decade is, “Inspire the World, Create the Future.”
- This new vision statement mirrors Samsung Electronics’ dedication to stimulating its communities by the three key strengths:
- New Technology, Innovative Products, and “Creative Solutions.”
- Through these efforts, Samsung hopes to contribute to a better world and a richer experience for all.
Person marketing
Person marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change the attitudes or behavior of target consumers toward particular people.
Example: Recall the last movie that you enjoy the most in the theater. Gucci, Hermes, Vertu, Burberry and Louis Vuitton are famous fashion brands that deal with customers personally. They make clothes and other products keeping in mind the taste of every individual.
Place marketing
Place marketing consists of activities undertaken to create, maintain, or change attitudes and behavior toward particular places.
Example: City marketing, region marketing, country marketing all fall under place marketing. Place marketing can have various benefits like:
- Improving local businesses.
- Attracting foreign businesses.
- Boosting tourism.
- Overall area development.
- Cultural uplift.
Social marketing
Social marketing uses commercial marketing concepts to influence individuals’ behavior to improve their well-being and that of society.
Example: To encourage nurses to support a mother’s choice to start breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth. The Department of Health (DH) in England uses strategic social marketing thinking to tackle lung disease. Also known as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), it currently kills over 30,000 people every year. That’s a higher death rate than breast and prostate cancer combined − but most people have never heard of it.
Product And Service Decisions
Individual Product and Service Decisions
In the development and marketing of individual products (and services), individual product decisions need to be made. These decisions apply to any kind of product and service and set the base for all other decisions.
A product attribute
A product attribute is a characteristic that defines a particular product and will affect a consumer’s purchase decision. Product attributes can be tangible (or physical in nature) or intangible (or not physical in nature).
- Quality
- Features
- Style and design: Color. Size. Design. Weight. Content. Smell. Taste. Feel.
Product quality refers to the characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy stated or implied customer needs.
- Total quality management
- Return-on-quality
- Quality level
- Performance quality
- Conformance quality
Product Features: Competitive tool for differentiating a product from competitors’ products.
For example, some ovens include features such as self-cleaning, smooth stovetops, warming bins, or convection capabilities.
Style describes the appearance of the product.
Design contributes to a product’s usefulness as well as to its looks.
Brand
Brand is the name, term, sign, or design or a combination of these, that identifies the maker or seller of a product or service.
Branding is the process where a business makes itself known to the public and differentiates itself from competitors. Branding naturally includes a phrase, design or idea that makes it easily identifiable to the public.
Packaging involves designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product.
Labels identify the product or brand, describe attributes, and provide promotion.
Product support services augment actual products.
Product Line Decisions
Product line length is the number of items in the product line.
For example, using the example of a manufacturer of teenager’s clothing, they might decide to offer 20 different designs of shirts for boys. This is their product line length for shirts.
Product Mix Decisions
Product Mix Decisions Product mix consists of all the product lines and items that a particular seller offers for sale.
Nature And Characteristics Of A Service
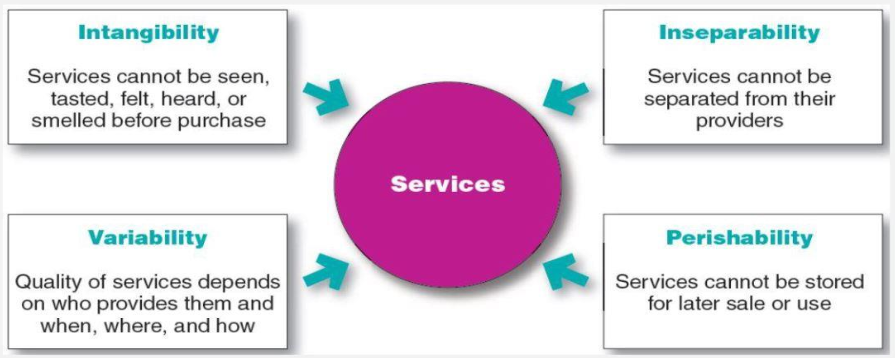
Marketing Strategies For Service Firms
In addition to traditional marketing strategies, service firms often require additional strategies.
- Service-profit chain
- Internal marketing
- Interactive marketing
Service-profit chain
Service-profit chain links service firm profits with employee and customer satisfaction.
- Internal service quality
- Satisfied and productive service employees
- Greater service value
- Satisfied and loyal customers
- Healthy service profits and growth
Internal marketing
Internal marketing means that the service firm must orient and motivate its customer-contact employees and supporting service people to work as a team to provide customer satisfaction.
- Social media profiles, company website, and other online activities;
- Job listings and promotion opportunities;
- Company benefits, perks, and work-life balance initiatives;
- Training, learning, and development sessions;
- Internal communications, including emails, instant messages, and phone calls;
- Workshops, brainstorming sessions, and meetings;
- Employee performance reviews, feedback opportunities, and spotlights;
- Company, project, and product branding and marketing;
- Company news, updates, milestones, and achievements.
Interactive marketing
Interactive marketing means that service quality depends heavily on the quality of the buyer-seller interaction during the service encounter.
Branding Strategy: Building Strong Brands
Question:
A> According to your point of view- What are the differences between Marketing and Branding?
Example: Philips
- 1890s- Entrepreneurs in a new light
- 1900s- The social pioneers
- 1910s-Growth and success through innovation
- 1920s-A leader in design
- 1930s- Changing the face of shaving
- 1940s- The modern age of broadcasting begins Founded in 1891 in Eindhoven, the Netherlands,
- 1950s-From products to experiences
- 1960s- Sound of the Sixties
- 1970s- Continued innovation in sound and vision
- 1980s-Leading the digital world
- 1990s-Human-centered design
- 2000s-Delivering new experiences
- 2010s-Leading in health technology
Brand Positioning
Marketers can position brands at any of three levels.
- Attributes
- Benefits
- Beliefs and values
Coca-Cola is a classic brand but with the flexibility for a fresh, modern take. The company’s marketing and advertising campaigns always stay true to the brand’s identity: refreshing and fun, while focusing on the positive experiences consumers have when enjoying Coca-Cola beverages. Coca-Cola inspires happiness and positivity.
All great things are simple, and many can be expressed in single words:
- Freedom
- Justice
- Honors
- Duty
- Mercy
- Hope
Brand Name Selection
- Suggests benefits and qualities
- Easy to pronounce, recognize, and remember
- Distinctive
- Extendable
- Translatable for the global economy
- Capable of registration and legal protection
Brand Sponsorship
- Manufacturer’s brand: Ford, Nestle, Coca-Cola, Apple
- Private brand-
- Licensed brand- A good example is Toyota and Lexus; the Lexus brand was introduced by Toyota into the US market because in that market, the Toyota brand was viewed as a value brand.
- Co-brand- Nike partnered with Apple for Apple Watch
How To Build A Brand?
In order to build a brand, businesses should complete FOUR STEPS:
1. Define your company’s identity
Knowing what you want your company to represent and what you want its purpose to be is the first step in building a brand. By envisioning what you want your company to be, you can start planning to make it a reality. For example, the owner of a makeup line might decide that they want their identity to be based around three principles: environmental responsibility, value and versatility. With your company’s identity in mind, you can plan marketing strategies for your products. In the case of the makeup line owner, these strategies might include an advertisement that promotes organic ingredients or tutorial videos that show three different ways to wear blush
2. Highlight your target audience
Honing in on your audience is important when cultivating your brand identity. Consider your audience’s age, gender, socio-economic status, culture and even geographic location. These factors will help influence the way you present your company to the public.
For example, if you own a car dealership in Albany, New York, you may identify your audience as men and women between the ages of 25-65 who are typically middle and upper class and live in and around Albany, New York.
3. Organize your company around desired identity
Structuring your company in accordance with your brand can help ensure that the promises you promote are being upheld. For example, a national bank says that they provide quality customer service 24 hours a day. To uphold this claim, they need to make sure that they have experienced, well-trained customer service representatives available day and night.
4. Don’t be afraid to revise
Once you commit to a certain company image, don’t be afraid to revise it. Your brand can evolve as your company grows and as you establish yourself within your industry.
For example, a travel agency has branded itself as an aid for domestic and international vacations. However, after seeing a trend in study, work and volunteer abroad programs, they expand their services to helping people plan and execute educational experiences abroad.
Why Is Branding Important?
Branding is important for the following reasons:
- Establishes your company within an industry: The right brand identity can potentially help you get established within your industry. This can also help you compete with those who offer similar services as your brand gets more recognition.
- Conveys your purpose to consumers: Your brand is also important because it helps convey the value that your products or services can provide for consumers. For example, if your cleaning products company has the slogan: “Less time for cleanup, more time for fun,” then you imply to consumers that your product line helps clean up messes fast so customers can do more of what they enjoy.
- Increases company awareness: Having a strong and recognizable brand could potentially attract new customers.
- Reminds existing customers of your products and services: Your brand can also help remind existing customers about what you have to offer. For example, McDonald’s drive-through windows.
What Makes A Good Brand?
Here are TWO KEY components that help contribute to a good brand:
- Logo: Your logo is an important part of your brand because it’s a visual representation of your company. A logo – typically includes a specific color scheme, shape or image. In some cases, a logo can be your company name with a font and color that reflects your company culture.
- Slogan: A slogan is a brief, clear message that showcases your company’s values. Your slogan should help establish an emotional connection to your company. You can have more than one slogan if you offer a variety of different services.
Nike: “Just do it.”
MasterCard: “There are some things money can’t buy. For everything else, there’s MasterCard.”
Samsung: “Do what you can’t.”
BMW: “The ultimate driving machine.”
Uber: “Move the way you want.”
Toyota: “Let’s go places.”
Burger King: “Have it your way.”
American Express: “Don’t live life without
References:
- https://securityboulevard.com/2020/03/improving-customer-experience-in-the-hospitalityindustry/
- http://www.worksupport.com/documents/sechap21.pdf
- https://www.brafton.com/blog/content-marketing/the-best-interactive-marketingexamples-of-2018/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7VOp-3PkzqY
- https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/best-cobranding-partnerships





